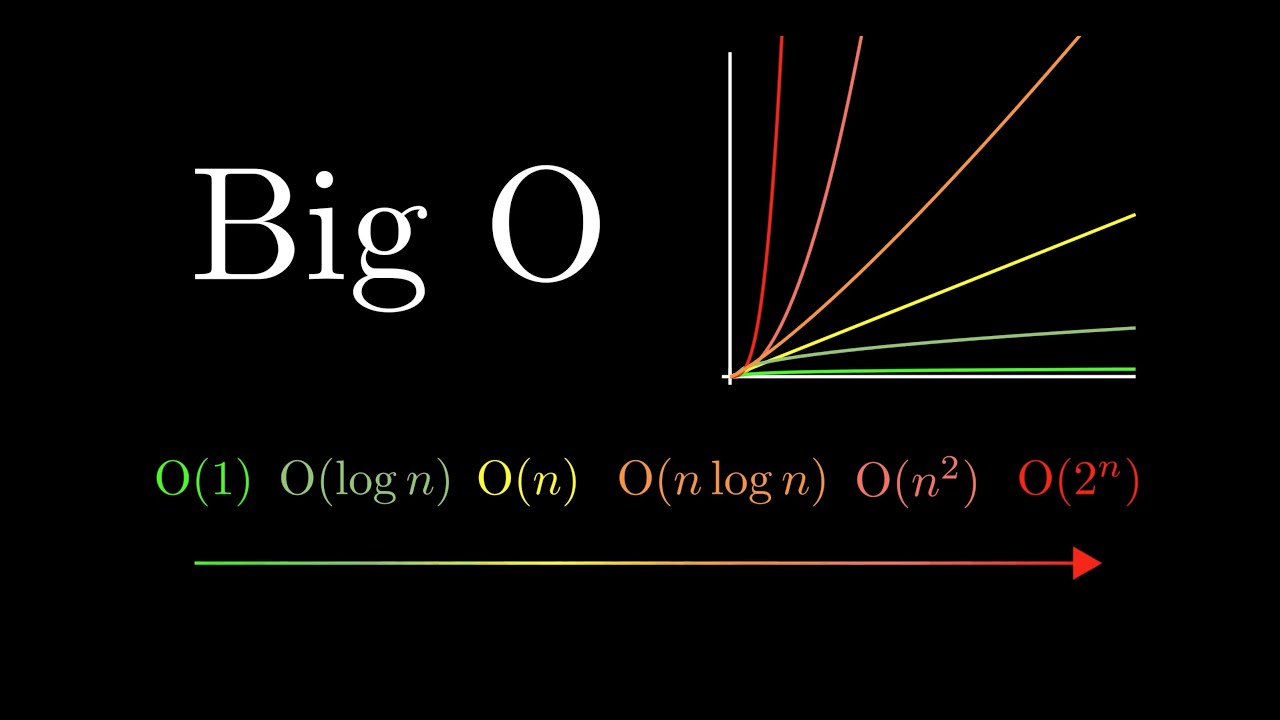
If you're preparing for technical interviews, understanding Big O notation isn't just helpful—it's essential. But let's be honest: many explanations of Big O notation feel like they were written for mathematicians, not developers. Let's change that with a practical, developer-friendly guide that you'll actually enjoy reading.
What is Big O Notation, Really?
Think of Big O notation as your algorithm's price tag. Just like you check prices when shopping, Big O helps you understand the "cost" of your code in terms of time and resources. It answers the crucial question: "How will my code perform as my data grows?"
Why Should You Care?
Before diving deep, let's address the elephant in the room: Why spend time learning this? Because:
- It's the universal language for discussing algorithm efficiency
- It helps you make informed decisions about your code
- It's a favorite topic in technical interviews
- Most importantly, it makes you a better developer
The Big O Hierarchy: A Practical Overview
Let's break down common Big O notations, from fastest to slowest, with real-world analogies:
O(1) - Constant Time
Imagine reaching directly into your pocket and pulling out your keys. Whether you have 1 or 100 keys in your pocket, the action takes the same time.
function getFirstElement(array) {
return array[0]; // Always takes the same time, regardless of array size
}
O(log n) - Logarithmic Time
Think of finding a word in a dictionary. You don't check every page—you split the book in half repeatedly until you find what you need.
function binarySearch(sortedArray, target) {
let left = 0;
let right = sortedArray.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
if (sortedArray[mid] === target) return mid;
if (sortedArray[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
O(n) - Linear Time
Like reading a book from start to finish. The time increases directly with the number of pages.
function findMax(array) {
let max = array[0];
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] > max) max = array[i];
}
return max;
}
O(n log n) - Linearithmic Time
Think of sorting a deck of cards using merge sort. You split the deck into smaller piles (log n) and then combine them back together (n).
function mergeSort(array) {
if (array.length <= 1) return array;
const mid = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
const left = mergeSort(array.slice(0, mid));
const right = mergeSort(array.slice(mid));
return merge(left, right);
}
O(n²) - Quadratic Time
Like checking every pair of socks in your drawer to find matches. As the number of socks increases, the time increases dramatically.
function bubbleSort(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < array.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
[array[j], array[j + 1]] = [array[j + 1], array[j]];
}
}
}
return array;
}
Common Interview Scenarios and How to Tackle Them
Scenario 1: Array Operations
When asked about array operations, remember these common complexities:
- Access: O(1)
- Search: O(n)
- Insertion/Deletion at end: O(1)
- Insertion/Deletion at beginning: O(n)
Scenario 2: Optimizing Nested Loops
Here's a common interview question: "How would you optimize this code?"
// Before: O(n²)
function findDuplicates(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
if (array[i] === array[j]) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// After: O(n)
function findDuplicatesOptimized(array) {
const seen = new Set();
for (const item of array) {
if (seen.has(item)) return true;
seen.add(item);
}
return false;
}
Space Complexity: The Other Half of the Story
While we often focus on time complexity, space complexity is equally important. Here's what you need to know:
Understanding Space Complexity
Space complexity measures the additional memory your algorithm needs relative to input size.
// O(1) space complexity
function sum(array) {
let total = 0;
for (const num of array) {
total += num;
}
return total;
}
// O(n) space complexity
function duplicate(array) {
return [...array, ...array];
}
Common Interview Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Not Considering Edge Cases Always discuss these scenarios:
- Empty input
- Single element
- Maximum input size
Focusing Only on Time Complexity Remember to discuss:
- Space-time tradeoffs
- Memory constraints
- System requirements
Missing Optimization Opportunities Look for ways to optimize using:
- Hash tables for O(1) lookup
- Binary search for sorted data
- Two-pointer technique for array problems
Practical Tips for Technical Interviews
1. Analyze First, Code Later
Before writing any code:
- Understand the constraints
- Consider multiple approaches
- Discuss tradeoffs with your interviewer
2. Use the "Think Aloud" Protocol
- Share your thought process
- Explain your reasoning
- Show your problem-solving approach
3. Pattern Recognition
Learn to recognize common patterns:
- Sliding window
- Two pointers
- Divide and conquer
- Dynamic programming
Real-World Applications
Big O isn't just for interviews. Here's how it applies in real development:
Database Queries
-- O(1) with proper indexing
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1;
-- O(n) without proper indexing
SELECT * FROM users WHERE name LIKE '%John%';
API Design
// O(n) - Could be problematic for large datasets
app.get('/api/users', (req, res) => {
const users = getAllUsers(); // Fetches all users
res.json(users);
});
// O(1) - Better for pagination
app.get('/api/users', (req, res) => {
const { page, limit } = req.query;
const users = getUsersWithPagination(page, limit);
res.json(users);
});
Practice Problems
To solidify your understanding, try analyzing these common scenarios:
- Finding all pairs in an array that sum to a target value
- Implementing a queue using two stacks
- Finding the longest substring without repeating characters
Next Steps
Ready to deepen your knowledge? Here's what to explore next:
Advanced Topics
- Amortized analysis
- Master theorem
- NP-completeness
Related Concepts
- Data structure implementations
- Algorithm design patterns
- System design basics
Practice Resources
- LeetCode problems tagged with "Big O"
- Interactive visualization tools
- Mock interview platforms
Want to master more technical interview topics? Check out our complete interview preparation guide, featuring hands-on exercises and real interview questions from top tech companies.
Remember: Big O notation isn't just about memorizing formulas—it's about understanding how your code scales. Keep practicing, and you'll start seeing patterns everywhere in your code. Happy coding! 🚀
